Record-low coal consumption in 2019
In the almost 50 years over which the Danish Energy Agency has been collecting energy statistics, the Agency has never registered a lower consumption of coal and coke in Denmark than in 2019, when observed consumption amounted to 39 PJ. This corresponds to just 5% of energy consumption. Coal consumption fell by 42.7% compared with 2018, while consumption of natural gas fell by 7.6%.
This trend is due to a general drop in observed energy consumption of 3.4%, increasing net imports of electricity from neighbouring countries, as well as higher consumption of renewable energy. Renewables covered 35.0% of the observed energy consumption in 2019, compared with 32.9% in 2018.
Drop in CO2 emissions from energy consumption
There was high wind energy production in 2019, and combined with the falling consumption of fossil fuels, this meant that observed CO2 emissions from energy consumption dropped last year by 5.7% compared with 2018. Adjusted for climate fluctuations and fuel consumption linked to foreign trade in electricity, CO2 emissions fell by 3.9% in 2019.
Since 2010, observed CO2 emissions from energy consumption have fallen by 34.1%, and adjusted emissions have been reduced by 22.6%.
Drop in oil and natural gas production
Primary energy production in Denmark fell last year by 10.3% as a result of a dramatic fall in the production of oil and natural gas of 11.4% and 25.7%, respectively. Production from the North Sea in recent years has shown a downward trend, but the temporary shutdown and redevelopment of the Tyra field from September 2019 and to the completion in 2022 has particularly affected gas production from Tyra and production and landfall transportation from a number of associated fields.
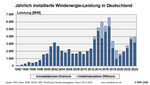
On the other hand, production of renewables has moved in the opposite direction, with an increase of 4.2%, corresponding to 7.2 PJ. The increase in the production of renewable energy is primarily due to an increase in production of wind power and biogas.
- Source:
- Danish Energy Agency
- Author:
- Press Office
- Link:
- en-press.ens.dk/...
- Keywords:
- Denmark, coal, sonsumption, energy consumption, Danish Energy Agency, statistics, CO2