News Release from windfair.net
Wind Industry Profile of
Climate Change: CO2 Levels Hit Record High in May
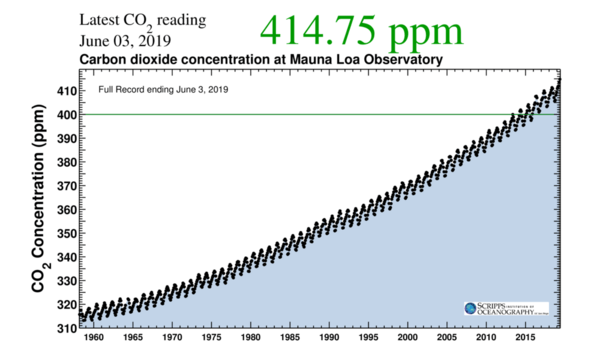
Climate change is happening fast - and there is proof. As the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) reports, there was a new record high amount of CO2 in the atmosphere in May. The measurement is the highest seasonal peak recorded in 61 years of observations on top of Hawaii’s second largest volcano Mauna Loa. From its location well above local human-generated influences, the observatory monitors the global atmosphere, including the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide. The location on the bare mountain top, far away from larger emitters, and the air currents over Hawaii make the data representative for the northern hemisphere of the earth.
Allthewile, it's the seventh consecutive year of steep global increases in concentrations of carbon dioxide according to NOAA and Scripps Institution of Oceanography. The 2019 peak value was 3.5 ppm higher than the 411.2 ppm peak in May 2018 and marks the second-highest annual jump on record. Monthly CO2 values at Mauna Loa first breached the 400 ppm threshold in 2014.
"It’s critically important to have these accurate, long-term measurements of CO2 in order to understand how quickly fossil fuel pollution is changing our climate,” said Pieter Tans, senior scientist with NOAA’s Global Monitoring Division. “These are measurements of the real atmosphere. They do not depend on any models, but they help us verify climate model projections, which if anything, have underestimated the rapid pace of climate change being observed."
The concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere increases every year, and the rate of increase is accelerating. The early years at Mauna Loa saw annual increases averaging about 0.7 ppm per year, increasing to about 1.6 ppm per year in the 1980s and 1.5 ppm per year in the 1990s. The growth rate rose to 2.2 ppm per year during the last decade. There is abundant and conclusive evidence that the acceleration is caused by increased emissions, Tans said.
The CO2 measurements at Mauna Loa (Image: Scipps Insitute of Oceanography)
The highest monthly mean CO2 value of the year always occurs in May, just before plants start to remove large amounts of the greenhouse gas from the atmosphere during the northern hemisphere growing season. In the northern fall, winter and early spring, plants and soils give off CO2, causing levels to rise through May. This cycle is now known as the Keeling Curve.
The rise in CO2 is nevertheless unambiguously caused by human activity, principally fossil-fuel burning, as Ralph Keeling, Scripps geochemist, says: "We know how much fossil fuel is converted into CO2 each year and emitted into the atmosphere. The CO2 doesn’t all stay there because some enters the ocean and some is taken up by photosynthesis, which ends up in land plants and various types of biomatter. It’s true that atmospheric CO2 has almost certainly been higher than present in Earth’s distant past, many millions of years ago. But because fossil-fuel burning is not natural, the recent carbon increases in the atmosphere, oceans and land biosphere cannot be natural either. And you are correct that even though the levels of CO2 in the air may not be unprecedented, the pace of rise probably is. Few if any natural processes can release fossil carbon into the atmosphere as fast as we humans are doing it now via the extraction and burning of fossil fuels."
- Author:
- Windfair Staff
- Email:
- press@windfair.net
- Keywords:
- NOAA, Scripps, Mount Loa, Hawaii, USA, observatory, CO2, atmosphere, huiman, cause, rising, carbon dioxide